The rel="canonical" attribute: why you should use it

Due to the peculiarities of the CMS or the dynamic parameters of the url, duplicate content may occur. However, you should not allow all duplicates to fall into the "field of view" of the search engine: for robots, you need to select only one, canonical page.
Why and when to use the rel="canonical" attribute

The rel="canonical" attribute is required to point search engines to the canonical page. A page with this attribute is considered a priority and is checked by search robots, while other duplicates are not affected. Google has allowed the use of such an attribute since 2009, while Yandex started using it two years later. A properly spelled tag allows robots to navigate from all copy versions to the canonical page without evaluating duplicates.
Also, thanks to the assigned rel="canonical" tag, you can eliminate duplicate content on the site, full or partial, as well as protect content from caching in web archives.
When should you use a tag?
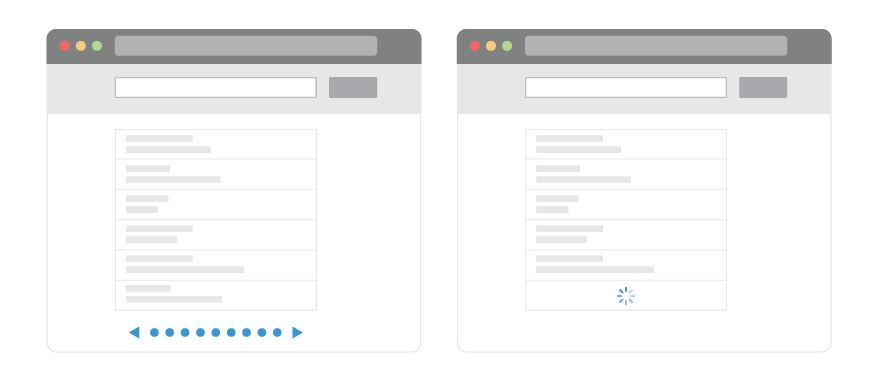
Here are the most typical cases in which it is imperative to choose a canonical page:
- pagination pages. In the case of selections on catalog pages, there are two options. If there is a “show all” section, then this page is made canonical. If not, then each of the possible samples will be considered canonical.
- Pages with UTM tags. If the page address contains UTM parameters like gclid, medium; content, source or _openstat, then the settings are made in such a way that the canonical link in this case is a URL without a UTM tag.
- Filtering pages. By themselves are specified by "canon".
- Duplicate content subject to placement on different domains. In this case, from each domain name where there are duplicates, you need to specify links to the main resource - the one that you have chosen for the index.
Highlights when using
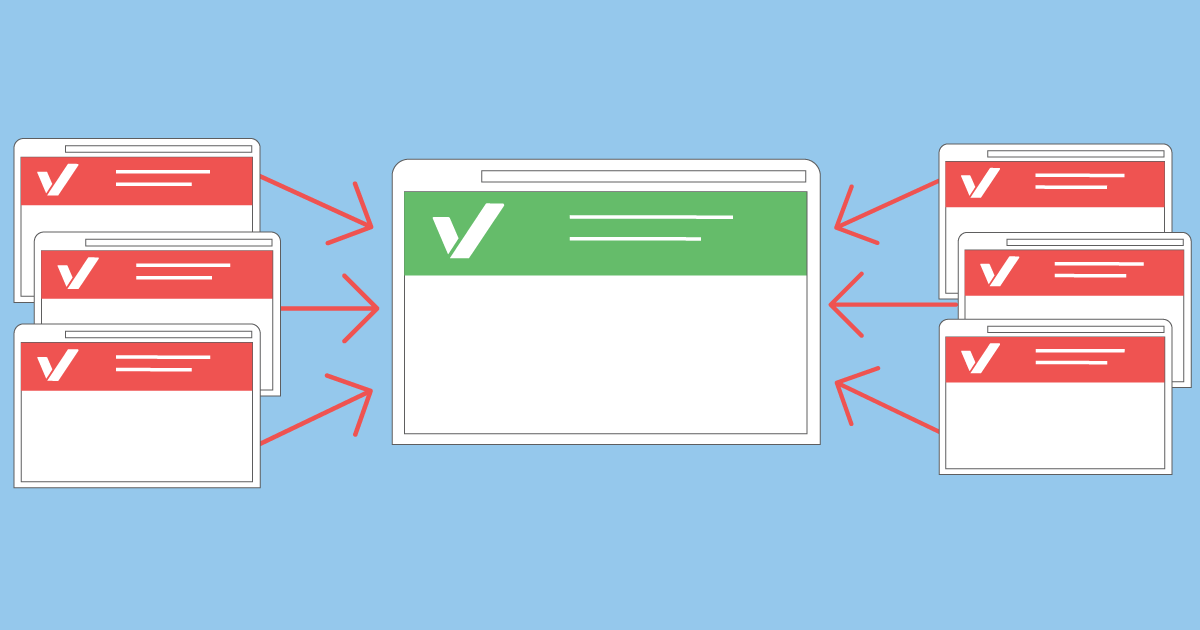
To avoid mistakes when setting the tag, you need to put only absolute links, where there is http:// or https://. Don't forget that it's not enough to just link to a page as canonical. It is important that the “header” of the page also indicates that it is the main one. Several canonical addresses affixed on one page at the same time will lead to a conflict - then the search robots themselves determine the "main" one, at their discretion. You also need to make sure that the links do not lead to a 404 error page. Chains of "canons" will also lead to confusion. In addition, the canonical tag itself is not a strict directive for search engines and may well be ignored by them. It is also important that Googlebots more often select pages on a secure https connection as the main ones.